Abstract
Introduction:
Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia (sAML), including AML transformation from an antecedent hematologic disorder or therapy related disease following radiation, chemotherapy, and/or immunosuppressive therapy (t-AML), and AML with myelodysplastic related changes (AML-MRC) are associated with worse outcomes. Prior studies of patients who transformed following hypomethylating agent (HMA) failure have suggested that induction therapy with liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine (CPX-351) or cladribine and high-dose cytarabine (CLAG)-based chemotherapy may improve outcomes compared to the standard of care 7 + 3. This is a retrospective comparison of CPX-351 and CLAG-based chemotherapy in patients with sAML and AML-MRC.
Methods:
Patients ≥18 years of age with treatment-naïve sAML or AML-MRC and received CPX-351 or CLAG-based chemotherapy at Moffitt Cancer Center between May 1, 2017 and October 5, 2020 were included. Patients who received prior therapy for sAML or AML-MRC were excluded. Response to induction therapy was assessed according to the ELN 2017 response criteria for AML. The primary objective was composite complete response (CRc), defined as complete response (CR), CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi), or CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRh) on bone marrow biopsy at time of count recovery. Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), relapse-free survival (RFS), 30- and 60-day mortality, rate of reinduction, incidence of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHCT), time to platelet (PLT) and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) recovery, and infection incidence and types during hospitalization. Fungal infections were defined according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) definitions for invasive fungal disease.
Results:
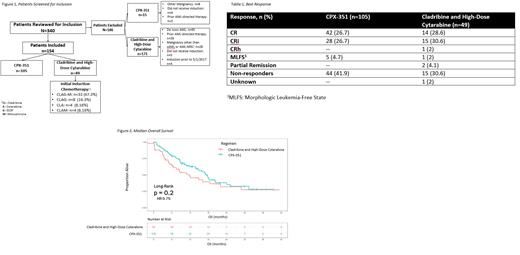
One hundred fifty-four patients met the inclusion criteria (CPX-351: n=105; CLAG-based chemotherapy: n=49) (Figure 1). Baseline chromosomal characteristics were similar between groups, except more patients in the CLAG-based chemotherapy group had abnormalities of chromosome 17p compared to the CPX-351 group by FISH (12.2% vs 2.2%; p=0.032). The CPX-351 group included more patients with AML-MRC (33.3% vs 12.2%; p=0.006) and myelodysplastic syndromes transformed to AML without prior HMA (18.1% vs. 2.04%; p=0.004) compared to the CLAG-based chemotherapy group.
The CRc was 53.3% with CPX-351 and 61.2% with CLAG-based chemotherapy (p=0.532). The rates of CR, CRi, and CRh were similar at time of recovery bone marrow biopsy between groups (Table 1). However, significantly more patients in the CPX-351 group received reinduction compared to those in the CLAG-based chemotherapy group (37.1% vs. 14.3%; p=0.007). The median OS was 17.1 months (95%: 14.6 to 24.0) with CPX-351 compared to 11.7 months (95% CI: 6.5 to 28.8) with CLAG-based chemotherapy (p=0.2) (Figure 2). HMA failure status strongly predicted for inferior OS in both cohorts in multivariable analysis (HR 2.37; 95% CI, 1.46-3.83; P<0.001). The RFS among patients with a CR, CRi, and CRh, was 13.8 months (95% CI: 9.2 to N/A) with CPX-351 and 14.9 months (95% CI: 6.6 to N/A) with CLAG-based chemotherapy (p=0.36). The incidence of alloHCT was similar between groups (CPX-351: 45.2% vs. CLAG-based chemotherapy: 42.2%; p=0.876) with a median OS that was not reached in either cohort. The incidence of relapse following alloHCT was 3.8% in the CPX-351 group and 8.2% in the CLAG-based chemotherapy group.
The 30-day and 60-day mortality rates were 2.9% and 6.7% for CPX-351 vs. 12.2% and 12.2% for CLAG -based chemotherapy, respectively (p=0.03 and p=0.35). The median time to PLT count recovery (>50,000/mcL) and ANC recovery (>1,500/microL) was longer with CPX-351 compared to CLAG-based chemotherapy: 41 days vs. 31 days, respectively (p=0.012) and 35 days vs. 32 days, respectively (p=0.0743). The incidence of ≥1 infection during hospitalization was similar between groups (CPX-351: 45.7%; CLAG-based chemotherapy: 49%).
Conclusion:
No significant difference in response or OS were found between CPX-351 and CLAG-based chemotherapy as initial therapy in treatment-naïve sAML and AML-MRC. However, CPX-351 was associated with a significantly lower 30-day mortality rate. HMA failure status strongly predicted outcomes in both cohorts.
Sweet: Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AROG: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kuykendall: Protagonist: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Prelude: Research Funding; PharmaEssentia: Honoraria; BluePrint Medicines: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy; CTI Biopharma: Honoraria; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Padron: Incyte: Research Funding; Kura: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Stemline: Honoraria; Taiho: Honoraria; Blueprint: Honoraria. Komrokji: BMSCelgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Acceleron: Consultancy; Taiho Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Geron: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; PharmaEssentia: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Lancet: BerGenBio: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy; ElevateBio Management: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Millenium Pharma/Takeda: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy. Talati: AbbVie: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Jazz: Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria; Astellas: Speakers Bureau. Sallman: Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Intellia: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Magenta: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aprea: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Syndax: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shattuck Labs: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal